How Quality Control Ensures Automotive Reliability
November 4, 2025
Why Quality Control Is Key to Building Reliable Vehicles
November 4, 2025Automation has reshaped nearly every industry — and vehicle manufacturing is no exception. In 2025, the automotive industry stands at the forefront of a technological revolution. From smart robots and AI-driven systems to data analytics and sustainable production, automation is transforming how cars are designed, built, and delivered. This change is not just about machines taking over manual work — it’s about smarter, faster, and more efficient production that ensures higher quality and lower costs.
Let’s explore how automation is redefining the future of vehicle manufacturing in 2025.
The Evolution of Automation in the Automotive Industry
Automation in vehicle manufacturing isn’t new. It began decades ago with simple assembly-line robots performing repetitive tasks like welding and painting. However, by 2025, automation has evolved far beyond that. Now, manufacturers use advanced robotics, machine learning, AI algorithms, and real-time data to make decisions on the production floor.
A Look Back: From Assembly Lines to Smart Factories
Henry Ford’s assembly line in the early 20th century revolutionized mass production. But today’s factories are “smart factories” — fully digital ecosystems where robots, sensors, and AI systems work together seamlessly.
These factories can self-correct errors, optimize energy usage, predict maintenance needs, and even adapt production lines based on consumer demand.
| Era | Key Development | Impact on Manufacturing |
| 1910s | Assembly Line | Mass production begins |
| 1970s | Industrial Robots | Automated welding, painting |
| 2000s | Computerized Systems | Precision and data integration |
| 2020s | AI & IoT Integration | Smart, connected factories |
| 2025 | Full Automation | Predictive, adaptive manufacturing |
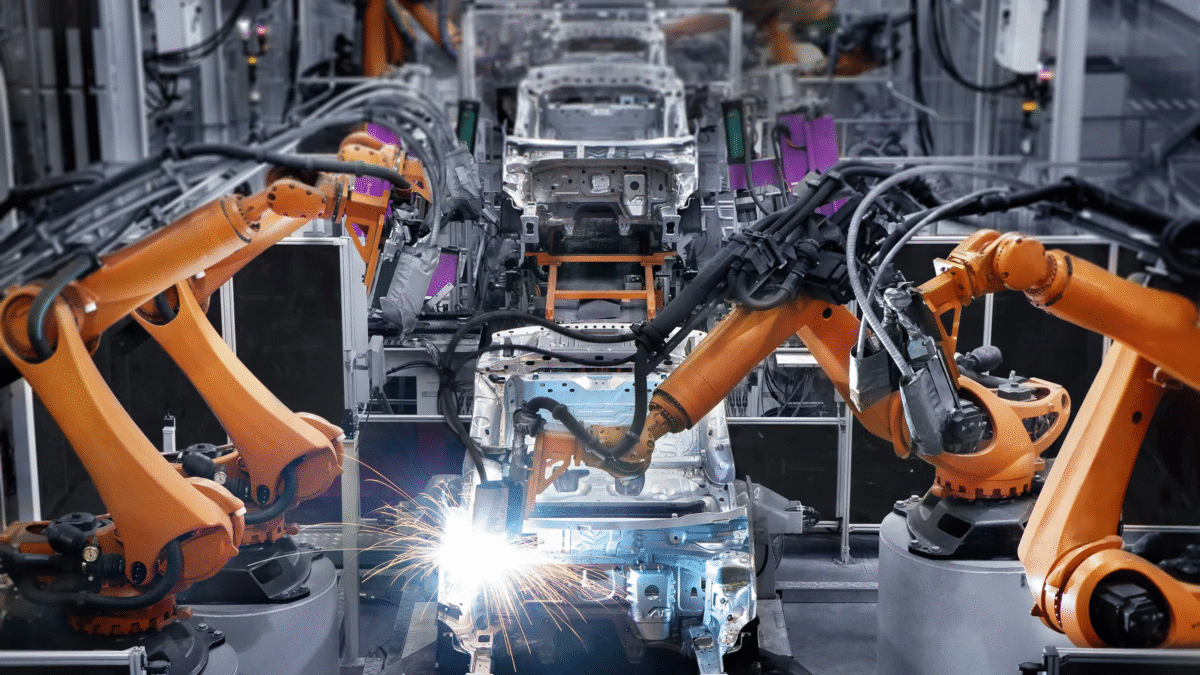
Robotics: The Heart of Automated Manufacturing
In 2025, robots have become the backbone of vehicle manufacturing. They handle everything from assembling body parts to installing complex electronic components. Unlike traditional robots that require human supervision, modern robots are collaborative (cobots) — designed to safely work alongside human workers.
Key Roles of Robotics in 2025
- Assembly Automation: Robotic arms handle precise assembly of car frames, engines, and interiors.
- Quality Inspection: Vision-enabled robots detect even the tiniest defects that humans might miss.
- Painting and Coating: Robots apply consistent coats, reducing waste and ensuring perfect finishes.
- Material Handling: Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) transport parts within the factory.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: AI-powered robots predict and perform maintenance tasks before breakdowns occur.
These innovations have dramatically improved efficiency, consistency, and safety — while freeing human workers to focus on innovation and creative problem-solving.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics
AI is the brain of modern automation. In 2025, every stage of vehicle manufacturing uses AI in some form. Through sensors, cameras, and analytics tools, AI monitors production lines in real-time and makes split-second decisions to ensure optimal performance.
How AI Is Used in Vehicle Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance: AI systems analyze machine data to predict potential breakdowns before they happen.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Smart systems forecast demand and adjust supply orders automatically.
- Design and Simulation: Engineers use AI to simulate car designs and test them virtually before production.
- Quality Control: Machine learning models analyze thousands of images to spot defects instantly.
In essence, AI reduces downtime, improves precision, and enhances decision-making across the board.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Connected Factories
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects machines, tools, and systems into one unified network. In 2025, vehicle manufacturing plants rely heavily on IoT sensors to track performance, temperature, pressure, and energy use.
For example, if a welding robot overheats, an IoT sensor instantly alerts the system, which can either adjust the operation or reroute the task to another machine. This ensures continuous, uninterrupted production.
Benefits of IoT in Manufacturing
- Real-time data sharing between systems
- Reduced human error and downtime
- Better energy efficiency
- Improved traceability of components
IoT-driven factories are not just efficient but also responsive — adapting to market needs almost instantly.
Automation and Sustainability
Sustainability is no longer optional — it’s a necessity. Automation helps automakers achieve their green manufacturing goals in several ways.
How Automation Supports Eco-Friendly Production
- Energy Optimization: Smart systems monitor energy use and reduce waste.
- Material Efficiency: Automated systems calculate exact material requirements, minimizing scrap.
- Recycling Integration: Robots can separate and reuse materials effectively.
- Emission Control: Sensors track emissions in real-time to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
In 2025, the combination of automation and sustainability has led to “green factories” — production units that not only make cars but also protect the planet.
Human Roles in the Age of Automation
One of the biggest myths about automation is that it replaces humans entirely. In reality, it transforms their roles.
In 2025, humans are no longer doing repetitive physical work but are taking on supervisory, analytical, and creative roles. For instance, technicians monitor automated systems, data analysts optimize performance metrics, and engineers design smarter manufacturing processes.
The shift has also created new career opportunities in robotics maintenance, AI system management, cybersecurity, and data science within the automotive industry.
| Traditional Role | Automated Role | New Human Role |
| Assembly Worker | Robot Assembler | Robotics Supervisor |
| Quality Inspector | AI Inspection System | Data Analyst |
| Machine Operator | Automated Machine | Automation Engineer |
This collaboration between humans and machines leads to a more productive, safer, and innovative workplace.
Challenges of Automation in Vehicle Manufacturing
While automation brings many benefits, it also presents challenges.
Major Challenges Include:
- High Implementation Costs: Setting up smart factories requires huge investments.
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: Workers need advanced training to operate AI and robotics systems.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Connected systems are vulnerable to hacking if not properly secured.
- Technology Integration: Older machines may not easily integrate with new automation systems.
Automotive companies in 2025 are addressing these challenges through partnerships with tech firms, workforce upskilling, and strong cybersecurity frameworks.
The Future: What’s Next for Automated Vehicle Manufacturing?
As we look ahead, automation will continue to evolve. Expect to see:
- Fully autonomous factories where human input is minimal.
- 3D printing integration for faster, customized vehicle parts.
- Blockchain for supply chain transparency.
- AI-driven design tools that innovate cars based on real-world data.
The ultimate goal is hyper-efficiency — manufacturing vehicles that are safer, cleaner, and built with near-zero errors.
Conclusion
Automation is no longer just a futuristic concept — it’s the reality driving vehicle manufacturing in 2025. Through robotics, AI, IoT, and sustainable technologies, the industry is producing smarter cars in smarter ways. Automation not only improves efficiency and precision but also reshapes the workforce, enhances quality, and supports environmental goals.
As we move further into the decade, one thing is certain — automation isn’t just transforming vehicle manufacturing; it’s redefining the entire automotive world.
FAQs
1. What is automation in vehicle manufacturing?
Automation in vehicle manufacturing involves using robots, AI, and smart systems to perform tasks such as assembly, inspection, and logistics, reducing manual labor while improving accuracy and speed.
2. How does automation improve vehicle quality?
Automation ensures consistent production by using AI-powered inspections and robotic precision, reducing human error and improving vehicle durability and safety.
3. Are humans still needed in automated factories?
Yes, humans play critical roles in supervising, programming, maintaining, and analyzing automated systems to ensure smooth operations.
4. What are the environmental benefits of automation in manufacturing?
Automation helps reduce waste, optimize energy use, and support recycling processes — leading to cleaner, more sustainable production.
5. What’s the future of automation in the automotive industry?
The future includes fully connected factories, AI-driven design, 3D-printed components, and autonomous production lines that operate with minimal human intervention.